What is Remote Desktop?
Remote Desktop
allows the graphical interface of a remote Windows system to be
displayed over a network onto a local system. In addition, keyboard and
mouse events on the local system are transmitted to the remote system
enabling the local user to perform tasks on the remote system as if they
were physically sitting at the remote system. Conversely, resources
(such as printers and disk drives) on the local system can be made
available to the remote system for the duration of the connection. This
remote control can be established in a number of ways, including over
wide area networks (WAN), local area networks (LAN) or over the
internet.
In the case of Windows Server 2008, this service is provided by
Terminal Services running on the remote systems and the
Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) client on the local system.
Terminal Services run in two different modes,
Administration and
Virtual Session.
Remote Desktop for Administration provides full administration
functionality to the remote administrator (including access to the
console session and visibility of notification messages). Remote Desktop
for Administration is the equivalent to working directly at the remote
system's console. In virtual session mode the user is subject to some
limitations such as the ability to install applications and view console
notification messages.
Windows Server 2008 imposes some administrator logon
restrictions. Specifically, a maximum of two administrators may be
logged on at any one time, either two logged on remotely, or one local
and one remote administrator. This assumes, however, that different
accounts are being used to log on. In other words, the same user may not
log on locally and remotely simultaneously.
Enabling Remote Desktop Administration on the Remote Server
As mentioned previously, remote desktop functionality on the server
is provided by Terminal Services. It is important to note, however, that
Terminal Services do not have to be explicitly enabled on the server in
order to support Remote
Desktop Administration.
In fact, all that needs to be done is to enable Remote Desktop
Administration. This is configured by opening the Control Panel from the
Start menu and selecting the
System icon (if the Control Panel is in
Control Panel Home mode this is located under
System and Maintenance). In the
Task section in the top left hand corner of the System page select
Remote settings to display the following properties window:
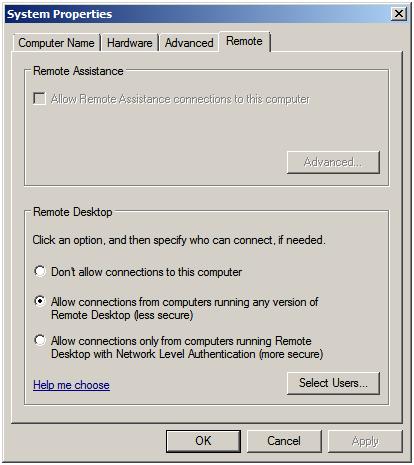
The Remote properties dialog provides a number of options. The default
setting is to disallow remote connections to the computer system. The
second option allows remote desktop connections from any version of the
Remote Desktop client. The third, and most secure option, will only
allow connections from Remote Desktop clients with Network Level
Authentication support. This typically will only allow access to systems
providing secure network authentication such as Windows Vista and
Windows Server 2008.
If the Windows Firewall is active, the act of enabling Remote
Desktop administration also results in the creation of a firewall
exception allowing Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) traffic to pass through
on TCP port 3389. This default port can be changed by changing this
setting in the Registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-tcp\PortNumber.
The easiest way to locate this registry key value is to execute
regedit from the
Run window or a command prompt, select
Edit - > Find and enter
RDP-tcp.
Controlling Remote Desktop Access
The default configuration for Remote Desktop is to allow all members
of the Administration group to connect remotely. Active Directory also
contains a
Remote Desktop Users group to which users may be added
to provide Remote Desktop access privileges. To provide users with
remote desktop access, open the
Control Panel -> System and Maintenance -> System -> Remote settings and click on the
Select Users button to invoke the
Remote Desktop Users dialog illustrated in the following figure:
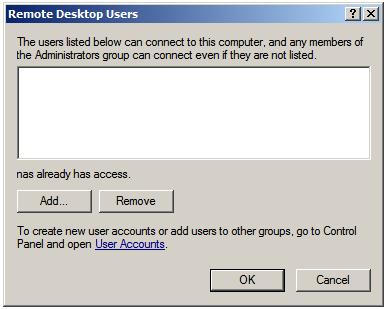
Note that users with administrative privileges do not need to be added
to this list; by default they already have Remote Desktop access. To add
additional users click on the
Add... button to display the
Select Users dialog. Enter the name of the user in the text box entitled
Enter object names to select and click on
Check names to list names that match the name entered. Select the appropriate name from the list. The following example shows user
Bill on server
winserver-2:

Click on
OK to apply the change. The new user will now appear in the list of users with Remote Desktop access on the
Remote Users screen. Click
OK to close this screen and click on
Apply in the System Settings screen. The specified user will now have remote desktop access to the system.
Remote Desktop Group Policy
A vast array of configuration options for Terminal Services is available through the
Group Policy settings. To access these values start the Group Policy Object Editor (open the Start menu and enter
gpedit.msc
into the Search box). In the Group Object Policy Editor navigate to
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows
Components\Terminal Services or User Configuration\Administrative
Templates\Windows Components\Terminal Services to access the range of
policy settings available.
Policy options include, amongst other options, items such as
control over resource redirection (printers, audio etc), setting session
time limits and security settings. A complete overview of all the
settings is beyond the scope of this book but almost without exception
the various settings are largely self-explanatory.
Starting the Remote Desktop Client
With the appropriate configuration tasks completed on the remote
system the next step is to launch the Remote Desktop Client on the local
system. The client can be run in either
administration mode which provides full integration with the console of the remote server, or
virtual session mode which provides some administrative privileges but does not provide console access or allow applications to be installed.
To invoke the Remote Desktop Client in virtual session mode either select
Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Remote Desktop Connection or enter the following in the Run dialog or at a command prompt:
mstsc
To start the Remote Desktop Client in administrator mode run the following command:
mstsc /admin
In either case the following initial screen will appear requesting details of computer to which the client is to connect:
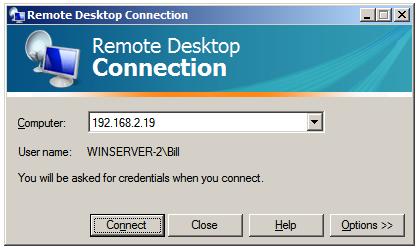
This can either be an IP address or a computer name. If previous connections have been established the
User name
field will be populated with the user name used in the preceding
session. If you need to log in as a different user this option will be
provided on the next screen which appears after the
Connect button is pressed:
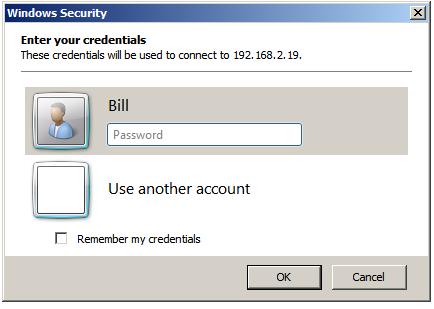
In this screen enter the password for the selected user (note that
remote desktop access is only available for user accounts which are
password protected). If a user other than the one displayed is required,
simply click on the
Use another account link and enter the
necessary details. Click on OK to establish the connection. After a
short delay the remote desktop will appear on the local computer screen.
Remote Desktop Client Configuration Options
The
Options>> button displayed on the initial screen of
the Remote Desktop Client provides six tabs, each containing a range of
configuration options:
- General - Allows login credentials to be configured and session information to be saved.
- Display - Configures the resolution and color settings to be used when displaying the remote desktop on the local system.
- Local Resources - Specifies which local resources
(sound, disk drives, printers etc) are to be made accessible to the
remote system during the Remote Desktop session. This page also provides
options to control the situations under which special key combinations
such as Ctrl-Alt-Del are interpreted by the local or remote systems.
- Programs - Allows specified programs to be automatically invoked each time a remote sessions is established.
- Experience - Controls which desktop features are enabled
or disabled for the Remote Desktop session. For example, over a slow
dial-up connection it is unwise to have the desktop background displayed
and font smoothing enabled. Either select the connection type and speed
to see recommended settings, or use Custom to configure your own
settings. This particular screen also provides the option to have the
connection automatically re-established in the event that a session is
dropped.
- Advanced - Enables and disables remote server
verification. This ensures that the remote server to which you are
connected is indeed the server you wanted. Also available are TS Gateway
settings. By default the Remote Desktop Client is configured to
automatically detect TS Gateway settings.
Remote Session Tracking
With Remote Desktop access implemented it is often useful to find out
at times who is logged into a system. This can be achieved using the
quser command-line tool. To obtain details of logged in users on a local system simply run
quser at a command prompt or in a Run dialog:
C:Users\Administrator> quser
USERNAME SESSIONNAME ID STATE IDLE TIME LOGON TIME
administrator 1 Disc 3:18 7/11/2008 12:36 PM
bill rdp-tcp#0 2 Active . 7/14/2008 9:11 AM
nas console 3 Active none 7/11/2008 12:58 PM
To obtain information for a remote system simply run
quser with the
/server:<hostname> command-line option. For example:
C:\Users\Administrator> quser /server:winserver-2
USERNAME SESSIONNAME ID STATE IDLE TIME LOGON TIME
administrator 1 Disc 3:22 7/11/2008 12:36 PM
bill rdp-tcp#0 2 Active . 7/14/2008 9:11 AM
nas console 3 Active none 7/11/2008 12:58 PM
Logging out from a Remote Desktop Session
When the Remote Desktop Client is exited by pressing the 'X' on the
control panel the remote session continues to run on the server even
though no client is connected. Next time the user connects the desktop
session will appear exactly as it was left before.
To end the session select
Start in the remote desktop session, click on the right arrow button in the bottom right hand corner of the menu and select
Log Off. This will close down the remote desktop session and close the remote desktop client.
Running Multiple Remote Desktops
Multiple concurrent remote desktops can be run and managed within a single window using the MMC
Remote Desktops snap-in. This may either be
snapped into the MMC or launched from the command-line or a Run dialog by typing:
tsmmc.msc
Once launched, right click on the
Remote desktops item in the tree in the left hand panel and select
Add a new connection from the menu. Once selected the
Add New Connection dialog will appear as follows:
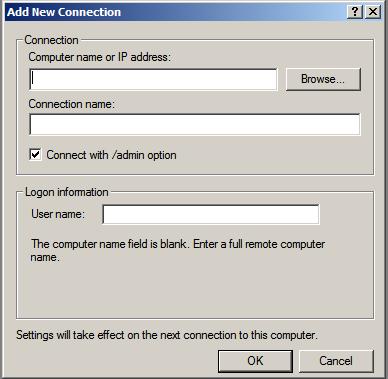
In this dialog enter the IP address or computer name of the remote
system together with the User name and the name to be assigned to this
connection (this is essentially the name by which this connection will
be listed and administered inside the Remote Desktops snap-in). For an
administrative session (as opposed to a virtual session) set the
Connect with /admin box. Click
OK to add the session to the snap-in. Once added, the session will appear in the left hand panel under
Remote Desktops. Repeat these steps to add connections to any additional remote systems required.
To establish a remote desktop connection, right click on the name of the session from the left hand panel and select
Connect
from the menu. The remote session will appear in the window. To start
another session simply right click on the session name and once again
select
Connect. To switch between sessions simply click on the
name of the session in the left hand panel and the corresponding desktop
will be displayed. The following figure illustrates two sessions
running in Remote Desktops:
To change configuration options for each session right click on the desired session in the left hand panel and select
Properties. This panel has a number of tabs which enable credentials, screen size and program start properties to be defined.